Ptasis (पलक गिरना) Sugery
Ptosis (also known as palpebral ptosis or droopy eyelid) refers to the condition where the upper eyelid droops or sags, partially or completely covering the eye. This condition can affect one or both eyes and can range from mild to severe. Ptosis can be congenital (present at birth) or acquired (developing later in life), often due to weakness or dysfunction of the muscle responsible for lifting the eyelid, known as the levator muscle.Ptosis surgery is performed to correct the drooping eyelid, restore normal eyelid function, and improve the appearance and vision of the patient. The goal of surgery is to lift the eyelid to its proper position and, in some cases, to correct any associated vision problems caused by the obstruction of the visual field.
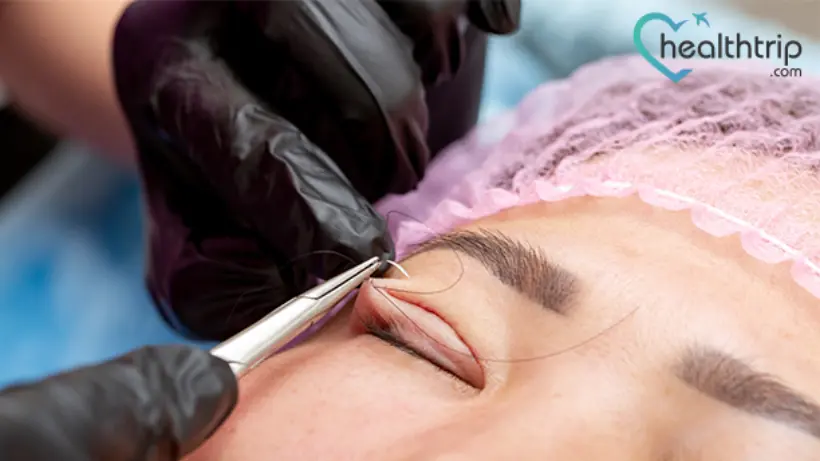
Indications for Ptosis Surgery
Ptosis surgery is typically recommended when the drooping eyelid interferes with vision or causes aesthetic concerns. Common indications for ptosis surgery include:
Obstruction of Vision
- If the drooping eyelid covers part or all of the eye, causing visual impairment, surgery is recommended to lift the eyelid and restore normal vision.
Eye Strain and Discomfort
- Patients who experience eye fatigue, headaches, or difficulty keeping the eye open due to ptosis may benefit from surgery to improve eyelid function.
Cosmetic Concerns
- Individuals who are self-conscious about the appearance of their drooping eyelid may opt for surgery to restore a more youthful and natural appearance.
Types of Ptosis Surgery
Ptosis surgery is performed to tighten or repair the levator muscle or adjust the eyelid to a more functional and aesthetically pleasing position. Several surgical techniques are used, depending on the severity of ptosis and the condition of the levator muscle.
Levator Resection
- This is the most common surgery for ptosis. The surgeon removes a portion of the levator muscle to shorten it, which increases its strength and lifts the eyelid. This technique is typically used in cases of mild to moderate ptosis where the levator muscle is still functional.
Levator Advancement
- In this procedure, the levator muscle is repositioned and reattached to a higher point on the eyelid to strengthen its function and lift the eyelid. This is often used when the levator muscle is weak but still functional.
Frontalis Suspension
- If the levator muscle is very weak or non-functional, frontalis suspension is performed. This technique involves attaching the eyelid to the frontalis muscle (the muscle responsible for lifting the brow). The frontalis muscle helps lift the eyelid, compensating for the loss of levator muscle function. This technique is commonly used in cases of severe ptosis or congenital ptosis.
Müller’s Muscle Resection
- This surgery targets the Müller’s muscle, a muscle that also helps in elevating the eyelid. It is a less invasive option and is often used in cases of mild ptosis.
