Service
Optical Coherence Tomography (O C P)
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging technique used to obtain high-resolution, cross-sectional images of biological tissues, particularly the retina and other parts of the eye. It is widely used in ophthalmology to diagnose and monitor a variety of eye conditions. By using light waves to capture detailed images, OCT provides insights into the structure and layers of the retina, optic nerve, and other ocular tissues, aiding in the early detection and management of eye diseases. revolutionized the field of ophthalmology by providing detailed insights into the eye’s internal structures. Its ability to diagnose and monitor eye diseases early has improved patient outcomes significantly. OCT is a critical tool for managing retinal conditions, glaucoma, and other ocular disorders, ensuring accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning.
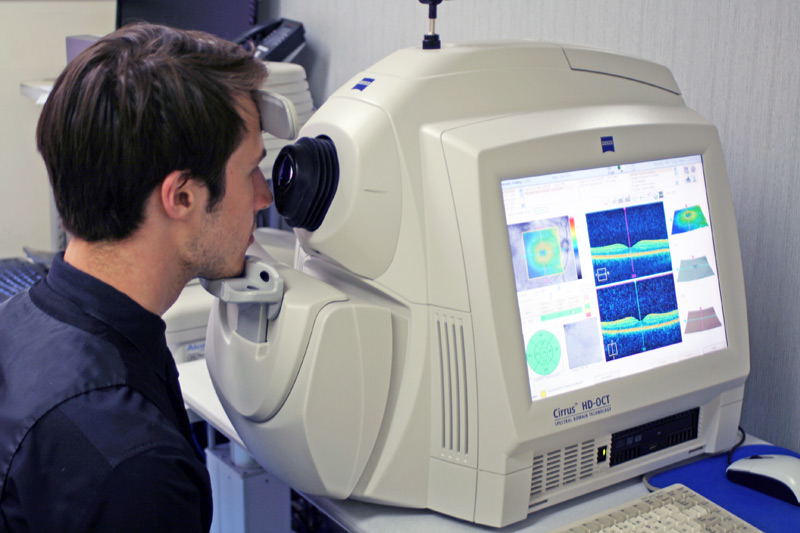
How OCT Works
OCT works by emitting low-coherence light waves that penetrate the tissue being examined. These light waves are reflected back from different layers of the tissue, and the interference pattern of the returning light is used to construct detailed cross-sectional images.
This imaging is analogous to ultrasound, but instead of sound waves, light waves are used, resulting in much higher resolution.
Applications of OCT
Retinal Imaging:
OCT provides detailed images of the retina, making it invaluable in diagnosing and managing conditions such as:- Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD): Helps monitor changes in the macula and the presence of fluid or new blood vessels.
- Diabetic Retinopathy: Detects swelling (macular edema) or bleeding caused by diabetes.
- Macular Hole and Epiretinal Membrane: Identifies structural issues in the retina.
Glaucoma Diagnosis and Monitoring:
- OCT measures the thickness of the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) and optic nerve head to detect early signs of glaucoma and monitor its progression.
Corneal Imaging:
- Used to assess corneal thickness and detect corneal dystrophies or keratoconus.
Anterior Segment Imaging:
- Evaluates the anterior segment of the eye, including the cornea, iris, and drainage angle, which is useful for glaucoma and other anterior segment conditions.
Optic Nerve Disorders:
- Monitors changes in the optic nerve, helping in the diagnosis of optic neuritis, papilledema, and other conditions.
