D.C.R ( नासूर ) Surgery
Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) is a surgical procedure performed to treat blocked or narrowed tear ducts. The tear ducts are responsible for draining tears from the eyes into the nasal cavity. When these ducts become blocked, it can lead to a variety of symptoms, including excessive tearing (epiphora), eye irritation, and recurrent eye infections. DCR surgery is done to create a new passage for the tears to drain properly, bypassing the blocked tear duct and restoring normal tear drainage.
In Hindi, the condition is often referred to as “नासूर” (nasoor), which is typically used to describe a blocked tear duct or an infected tear sac.
Symptoms of Blocked Tear Ducts
Excessive Tearing (Epiphora)
- The most common symptom of a blocked tear duct is excessive tearing, where the eyes produce more tears than can drain away.
Eye Irritation or Discomfort
- People with blocked tear ducts often experience irritation, redness, or a feeling of pressure around the eyes.
Frequent Eye Infections
- Blockages in the tear duct can lead to the accumulation of bacteria and result in recurrent eye infections or discharge.
Mucus Discharge
- A thick, yellow or greenish discharge from the corner of the eye is another symptom of blocked tear ducts, often seen with dacryocystitis (infection of the tear sac).
Indications for DCR Surgery
Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) surgery is recommended when other treatments, such as massage, antibiotics, or tear duct probing, do not provide relief from the symptoms of a blocked tear duct. Common indications for DCR surgery include:
Chronic Excessive Tearing
- When tearing becomes persistent and uncontrollable, even after trying non-surgical treatments, surgery may be necessary.
Frequent or Recurrent Eye Infections
- If the blockage is causing chronic infections or inflammation in the tear duct or tear sac, surgery may be needed to prevent further damage and complications.
Irritation or Pain Around the Eyes
- In cases where the blockage is causing significant discomfort, especially with the buildup of mucus or pressure in the eye, DCR surgery can help resolve these issues.
Failure of Conservative Treatments
- If initial treatments (such as tear duct probing or nasal steroids) fail to alleviate the symptoms of a blocked tear duct, DCR surgery becomes a more effective solution.
DCR Surgery Procedure
Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) is performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the patient’s age and the complexity of the case. The procedure involves creating a new drainage pathway for tears from the tear sac to the nasal cavity. There are two main techniques for performing DCR surgery:
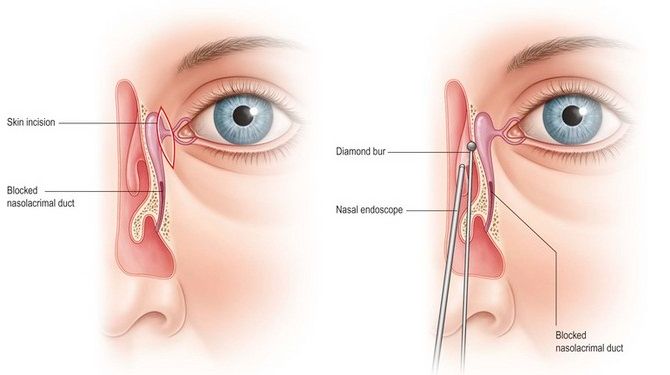
External DCR (Traditional Approach)
- The external approach is the most common technique. In this method:
- An incision is made on the skin next to the nose, near the inner corner of the eye.
- The surgeon creates a small opening into the tear sac and connects it to the nasal cavity, bypassing the blocked tear duct.
- A stent or tube may be placed temporarily to keep the new passage open during the healing process.
- The incision is then closed with sutures.
- The external approach is the most common technique. In this method:
Endoscopic DCR (Minimally Invasive Approach)
- The endoscopic approach is a less invasive method, performed through the nose without the need for external incisions.
- A small endoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera) is inserted into the nostrils to access the tear duct.
- The surgeon uses specialized instruments to create a new passage between the tear sac and the nasal cavity.
- This method avoids visible scarring and is preferred in certain cases, especially in adults and when there are no significant facial abnormalities.
- The endoscopic approach is a less invasive method, performed through the nose without the need for external incisions.
